962 Million USD Raised by China Edtech in 2019 Q3
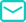
In the last three months, the capital market in China’s education industry has been presenting relative prosperity. 72 deals from China Edtech ventures have raised around 962 million USD (6.816 billion RMB), based on the data disclosed. Overall, STEAM, early childhood education, and K12 learning are the top 3 sub-sectors where the funds are concentrated. Most of the Chinese data in this piece are from EDU Insight.Overview: capitals invest predominantly at the start-up and early stagesThe number of financing deals taking place each month is stable, but the monthly amount has dropped drastically. The number of deals in September dropped by just one from August, but only raised 732 million yuan, which is one-third the total amount from the prior month.Regarding the financing round of deals in each sub-sector, apart from Bright Scholar’s US$300 million bond offering, the series distribution of other deals can be seen from the above chart. We can conclude that start-ups or projects at early financing stages are more favored by venture capitals, except in K12 track. Approximately 70% deals closed in competence-based learning and vocational education sectors are before B round.Among the 72 financing deals disclosed in Q3 of 2019, competence-based learning (24 deals), early childhood education (15) and K12 (12) are the top 3 sub-sectors, followed by vocational education (12), service providers (4), higher education (2) and language learning (3). K12 learning has witnessed a noticeable decline compared to the first half of this year, although still ranks among the top three sub-sectors. Competence-based learning jumps to the first place.The chart above reveals the top 5 deals in Q3 2019, and we can see that two of them are sparked from the mathematical thinking track. Huohua Siwei raised $85 million in their Series D round of financing, which is the largest deal in the history of China’s mathematical thinking market so far. VIPThink completed its Series B round of financing by raising hundreds of millions yuan, led by New Oriental.In terms of the overall financing amount regional distribution, the funds are still concentrated in first-tier cities. Enterprises that secured funding in Q3 are mainly based in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen. It is worth noting that the “Government Work Report 2019” has clearly proposed the development of “Internet + Education” in order to promote the sharing of education resources. Hence, with relevant policies laid out, and already highly saturated online education market in first- and second-tier cities, e-learning companies will find more opportunities when penetrating the immature market in third- and fourth-tier cities.Deep dive: competence-based education is still on the rise thanks to policy supportThis past July, the Chinese government went all-in on education reform, creating policies that give more benefits and incentives to competence-based learning players, which enhanced the development of physical education in particular, and underlined clear implementation requirements. The document pointed out that not only physical education subject scores be included in the high school entrance examination, more effort should also be put on campus football training. In addition, the government encouraged social organizations to provide students with high-quality sports services, giving greater opportunity to B2B companies eyeing the school market.And new categories of competence-based learning such as “handwriting training”, has attracted much attention from venture capitals. Xiaobohu Writing Class, which provides short video calligraphy writing classes on WeChat for children aged 6 to 13, has completed its seed round of financing with millions of yuan. Hexiaoxiang, a calligraphy education provider for children, has raised 200 million in its Series B round of financing.The government required students in grades 3–9 be educated in calligraphy at school, as early as 2011. But the market did not capitalize upon this opportunity until 2017, when the Ministry of Education stipulated that calligraphy, meaning “handwriting training”, should be attached more importance than Chinese language learning, mathematics and English. It is involved in the plan of carrying forward Chinese traditional culture. In 2018, 16 colleges and universities across the country established calligraphy major studies, and some provinces have highlighted that Chinese traditional culture should be involved in the scope of high school entrance examination starting 2019. At the current stage, the handwriting training market is still on the rise, with large room and broad prospects for enterprises to vie for potential market shares.As mentioned above, two of the top 5 deals in Q3 took place in the mathematical thinking sector. The large amount of funds poured into this track has given rise to an extremely crowded market. This past July, the Ministry of Education along with other three departments also issued the “Working Plan on Strengthening Mathematical Science Research” (《关于加强数学科学研究工作方案》), which highlights the improvement of mathematics learning as a national strategy. Moreover, because of the government’s initiative on alleviating academic burdens, the sector of mathematics thinking with both attribute of competence-based education and school subject-based learning will have lots of potential where players may usher in the stage of fierce competition in the near future.




Related Articles